- Key Takeaways
- The Importance of Moving and Handling in Healthcare
- Key Elements of a Moving and Handling Policy
- Effective Moving and Handling Techniques
- Benefits of Proper Moving and Handling Practices
- Key Risks Involved in Moving and Handling
- Essential Moving and Handling Techniques
- Equipment for Safe Moving and Handling
- Training and Compliance
- Implementing a Moving and Handling Policy
- Special Considerations for Different Care Settings
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
In the world of healthcare, ensuring the safety and well-being of both patients and caregivers is paramount. Moving and handling in healthcare refers to the methods and practices used to assist patients with mobility-related tasks while minimising the risk of injury. These tasks can range from helping a patient get out of bed to transferring them from a wheelchair to another seat or repositioning them in a comfortable posture.
Understanding what moving and handling in care entails is crucial for healthcare providers. This practice involves not only physical actions but also the implementation of policies and techniques designed to prioritise safety and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Moving and handling in healthcare involves safely transferring individuals with limited mobility while preserving their dignity and independence, requiring evidence-based techniques and clear communication.
- Proper moving and handling techniques reduce injury risks for both patients and caregivers, enhancing safety, overall quality of life, and emotional well-being.
- A comprehensive moving and handling policy, along with regular training, risk assessments, and equipment maintenance, is essential for ensuring safety and compliance in care environments.
The Importance of Moving and Handling in Healthcare
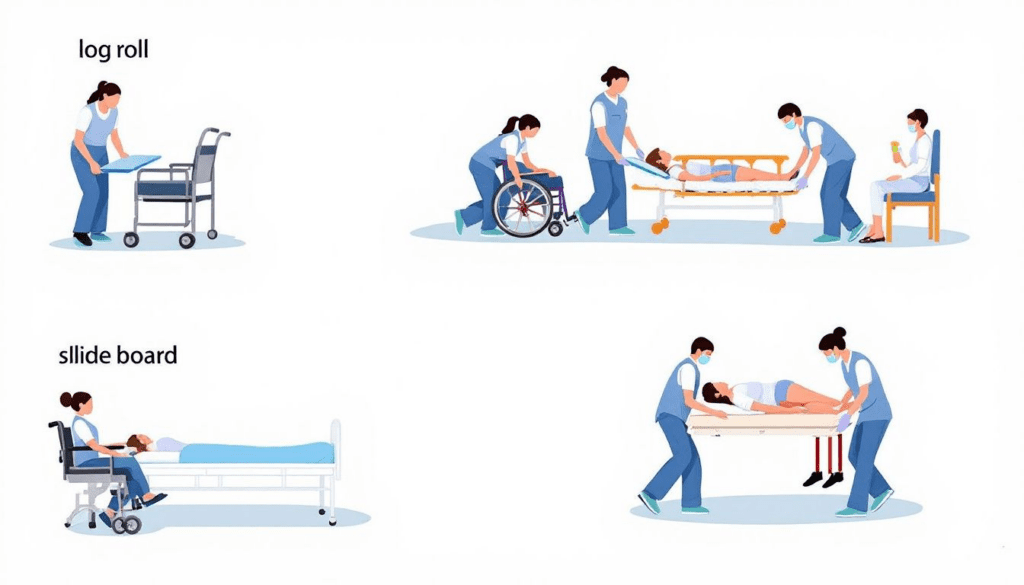
Proper moving and handling are integral to maintaining a high standard of care. Poorly executed techniques or a lack of adherence to a moving and handling policy can lead to significant consequences, including:
- Injuries to Patients: Improper handling can cause discomfort, bruises, or even severe injuries, particularly for individuals with mobility challenges or fragile health conditions.
- Caregiver Injuries: Healthcare workers often face risks such as musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) from repetitive strain or lifting heavy loads without proper support.
- Reduced Quality of Care: When moving and handling tasks are not performed correctly, it can compromise the patient’s dignity and overall experience.
Key Elements of a Moving and Handling Policy
A comprehensive moving and handling policy is essential for ensuring consistency and safety in healthcare settings. Key components often include:
- Risk Assessments: Evaluating the specific needs of each patient and identifying potential risks associated with their care.
- Training and Education: Providing healthcare staff with the knowledge and skills required for safe moving and handling techniques.
- Use of Equipment: Encouraging the appropriate use of aids such as hoists, slide sheets, and transfer boards to reduce physical strain.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically assessing the effectiveness of moving and handling practices to adapt to changing circumstances or patient needs.
Effective Moving and Handling Techniques

Employing proper moving and handling techniques is fundamental to ensuring safety and comfort. Here are some commonly recommended practices:
- Maintaining Good Posture: Caregivers should always adopt correct postures when performing any moving and handling technique..
- Using Teamwork: For tasks that require more strength or coordination, working in pairs can help distribute the load and improve safety. There must always be an identified team leader. The office for national statistics say that 80% of accidents are when handling in a team. ( Source ONS 2023)
- Minimising Manual Lifting: Wherever possible, mechanical aids should be used to reduce the physical burden on caregivers.
- Communicating Clearly: Explaining the process to the patient and involving them as much as possible ensures a smoother and more dignified experience.
Benefits of Proper Moving and Handling Practices
Adopting effective moving and handling techniques offers numerous advantages, including:
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Reducing the likelihood of falls or injuries during transfers and other mobility-related tasks.
- Improved Caregiver Well-being: Minimising the risk of physical strain and long-term injuries among healthcare workers.
- Greater Patient Comfort: Ensuring that patients are moved or repositioned with care and respect.
- Compliance with Regulations: Meeting legal and organisational standards for workplace safety and patient care.
Key Risks Involved in Moving and Handling
Moving and handling in care come with several risks, primarily due to the physical nature of the tasks involved. Common risks include strains, sprains, back pain, cuts, bruises, overexertion, and psychological stress. Failing to adhere to moving and handling legislation significantly increases the risk of these injuries.
Individuals requiring help with moving and handling often have health issues that limit their mobility, further increasing the risk of accidents. Safe moving and handling techniques involve using appropriate equipment and maintaining a stable posture to minimise injury risk.
Common Injuries
Poor moving and handling practices can lead to a variety of injuries, with back pain and musculoskeletal issues being the most common. Techniques such as drag lifts can cause skin tears and shoulder injuries, which are preventable with proper training and equipment use. A drag lift should be considered as abuse
To reduce the risk of manual handling injuries, routine manual lifting of patients should be avoided. In the case of infants and small children this may not be appropriate and subject to risk assessment and training may be appropriate.
Risk Assessment
Thorough risk assessments are paramount to ensuring safety in manual handling risk assessment and moving and handling tasks. These assessments help identify specific hazards and potential injuries, allowing for the implementation of appropriate control measures. Both generic and individual risk assessments are crucial for identifying potential injury sources and outlining actions to prevent them.
Thorough risk assessments are legally required. Regular reviews and updates of risk assessments are necessary, particularly when circumstances within care environments change.
Risk assessments must be conducted by a “competent person” (Source HSE)
Essential Moving and Handling Techniques
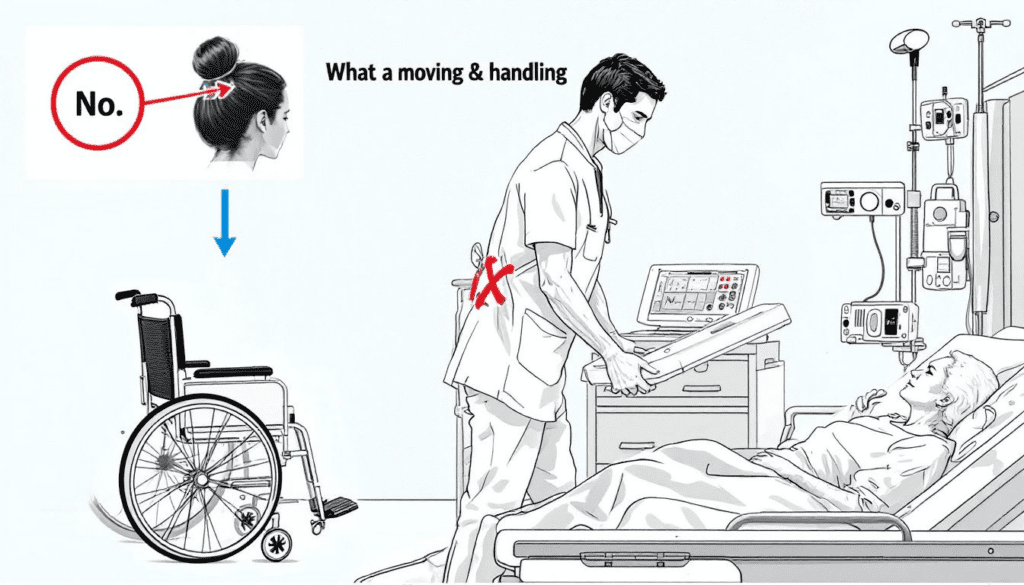
Specific techniques significantly enhance the safety and effectiveness of care workers during manual handling tasks. Care workers should utilise techniques that minimise risk and enhance safety during moving and handling tasks.
Standing aids and slide sheets are examples of equipment that facilitate easier transitions and reduce the risk of injury.
Use Your Legs, Not Your Back
Using leg muscles instead of back muscles is a fundamental technique that helps reduce the likelihood of musculoskeletal injuries during patient transfers. Leg muscles provide better support and leverage, preventing strain on the back and ensuring safer movement.
This technique is essential for proper handling techniques and carrying loads safely.
Get Close to the Patient
Being close to the patient during transfers minimises the risk of strain and enhances control. Positioning oneself near the patient reduces the need to stretch, allowing for better control and stability during the transfer process.
This approach is crucial for safe handling and preventing injuries.
Communicate & Coordinate
Effective communication among caregivers is crucial for executing safe and efficient patient movements. Clear communication ensures synchronised movements, which is essential for safe handling. Care organisations must provide adequate training to ensure caregivers understand the importance of communication and coordination during handling tasks.
Equipment for Safe Moving and Handling
A variety of equipment tailored to specific needs is available for moving and handling. Equipment such as hoists, slide sheets, and standing aids can effectively replace manual lifting, ensuring safer and more efficient patient movements. Specialist equipment is vital for preventing injuries and promoting independence.
Hoists and Transfer Boards
Hoists and transfer boards are essential pieces of equipment for safe moving and handling. Hoists can be classified into several types, including sit-to-stand lifts and overhead lifts, based on the specific needs of the individual.
Using hoists and transfer boards helps ensure safer and more efficient patient movements, reducing the risk of injuries.
Slide Sheets and Standing Aids
Slide sheets and standing aids are designed to assist in the moving and handling of individuals, promoting safety and efficiency. Slide sheets minimise friction, making repositioning patients easier and reducing the risk of injury.
Standing aids facilitate easier transitions for individuals, enhancing mobility while ensuring safety.
Maintenance and Safety Checks
Regular inspections of moving and handling equipment are crucial for maintaining their operational safety and reliability. Identifying wear and ensuring functionality through regular inspections are essential for preventing handling accidents and ensuring safe techniques.
All equipment should undergo regular maintenance and safety checks to ensure functionality.
Training and Compliance

Employers are legally obligated to create a safe working environment to minimise injury risks from manual handling. A moving and handling policy must outline the organisation’s commitment to managing risks related to moving and handling activities.
Training for staff is a critical component of the moving and handling policy, ensuring they are knowledgeable about safe practices and equipment.
Components of Moving and Handling Training
Training in moving and handling is structured as a combination of classroom theory and practical experience. Both generic and individual risk assessments are important for identifying moving and handling needs and ensuring safe practices.
Monitoring the implementation of these assessments is crucial for maintaining safety.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Legislation and guidelines ensure safety for employees and service users during moving and handling. The Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) and Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations (PUWER) apply LOLER for kit such as hoists and PUWER for kit such as a wheelchairs.
Adopting proper moving and handling procedures ensures caregivers remain compliant with health and safety regulations.
Implementing a Moving and Handling Policy
A moving and handling policy is essential to ensure that tasks are conducted safely and correctly. Employers are obligated to provide a safe working environment for their staff during moving and handling tasks.
Organisations must implement effective procedures for reporting concerns related to staffing, equipment, and policies.
Policy Development
Developing a comprehensive moving and handling policy is crucial for ensuring the safety of both patients and caregivers. This policy should include a detailed handling plan that specifies the equipment needed for safe moving and handling. Conducting thorough risk assessments is vital to identify potential hazards and implement appropriate control measures. Involving staff in the policy development process ensures that the policy meets the practical needs of care providers and service users, fostering a sense of ownership and compliance.
A well-structured policy outlines clear responsibilities for staff regarding moving and handling procedures. This includes specifying the types of equipment to be used, the training required, and the procedures for reporting and investigating incidents. By clearly defining these roles and responsibilities, the policy helps to ensure that all staff are aware of their duties and can carry out their tasks safely and effectively.
Monitoring and Review
Regularly reviewing the moving and handling policy ensures alignment with best practices and regulatory changes. These reviews should consider any changes in the care environment, such as new equipment or changes in patient needs, to ensure that the policy remains relevant and effective. Maintaining an updated policy is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of both patients and caregivers.
Periodic review and updates of risk assessments are essential to maintain safety. This ongoing evaluation helps to identify any new risks and implement appropriate control measures to prevent accidents and injuries. By keeping the policy and risk assessments up to date, organisations can ensure that they are providing the highest standard of care and safety for their patients and staff.
Special Considerations for Different Care Settings
Moving and handling practices must be adapted to the specific needs and environments of the individuals being assisted. In children’s care environments, for example, safety and comfort are paramount, requiring specialised techniques suited for younger, often smaller patients. Flexibility in mobility plans is essential to adapt to the unique needs of children, allowing them to achieve optimum independence while minimising risks for caregivers.
Community care presents its own set of challenges, necessitating personalised assessments and plans to accommodate diverse mobility and health needs during moving and handling tasks. Community care staff must have access to adequate resources and training to ensure effective moving and handling practices.
By adapting moving and handling practices according to the specific challenges of the care environment, caregivers can provide safe and high-quality care.
Children’s Care Environments
In children’s care environments, it is crucial to ensure flexibility in mobility plans to cater to their unique needs. This flexibility allows children to achieve optimum independence while minimising risks for caregivers. When developing mobility plans for neonates with complex care needs, consideration of attached equipment is necessary to ensure safety and comfort.
Specialised techniques and equipment are often required to handle the smaller and more delicate bodies of children safely. This includes using appropriately sized hoists, slide sheets, and other handling aids designed specifically for paediatric care. Ensuring that healthcare workers are trained in these specialised techniques is essential for providing safe and effective care in children’s environments.
Community Care
Community care settings require personalised assessments and plans to accommodate the diverse mobility and health needs of individuals. Moving and handling equipment should be provided based on the outcome of the risk assessment to ensure the safety and well-being of service users. Local councils can assist by providing equipment and guidance for safe moving and handling.
Adequate resources and training are essential for community care staff to manage moving and handling tasks effectively. This includes ensuring access to equipment such as hoists, slide sheets, and standing aids, as well as providing regular training and updates on safe handling practices.
By addressing the specific challenges of community care, caregivers can provide high-quality, personalised care that meets the needs of each individual.
Summary
Moving and handling in care are critical components of providing safe and effective care for individuals with limited mobility. Proper techniques, adequate training, and the use of specialised equipment are essential to prevent injuries and ensure the well-being of both patients and caregivers. By implementing comprehensive policies and regular reviews, care organisations can maintain high standards of safety and quality. The importance of moving and handling cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the dignity, independence, and quality of life of those in care. Let us strive to make every move a step towards better care.
At Solutions Training, we understand the importance of moving and handling in care. Our comprehensive training programmes are designed to equip healthcare professionals with the skills they need to perform these tasks safely and effectively. Contact us today to learn more about our tailored solutions. We have decades of experience in the health, social care, hospice, ambulance, and fire sectors, as well as case studies, to prove that our interventions reduce risks.


